The landscape of corporate sustainability reporting is undergoing a significant transformation, primarily driven by the European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). This directive marks a pivotal moment for companies, demanding a more robust and transparent approach to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting. For businesses, especially those in the B2B tech consulting sector, understanding and navigating these changes is crucial for compliance, growth, and long-term sustainability.
Understanding ESG and Its Strategic Importance
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors have become central to business strategies, influencing investment decisions, stakeholder relations, and overall corporate reputation. Companies with strong ESG practices are not only better positioned to attract top talent but also to drive long-term growth and innovation.
1. Strategic Importance:
- ESG factors are increasingly shaping business strategies, with investors and stakeholders demanding greater transparency and accountability.
- Companies with robust ESG practices can enhance their reputation, attract top talent, and drive sustainable growth.
2. Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management:
- Effective ESG management helps companies stay ahead of regulatory requirements, including the CSRD, mitigating potential risks.
- Compliance with global sustainability standards reduces legal and financial repercussions, ensuring a company’s long-term viability.
3. Sustainable Growth and Innovation:
- Embracing ESG principles can unlock new market opportunities, drive innovation, and improve operational efficiencies.
- Sustainable practices contribute to resilience and competitiveness in a rapidly changing business environment.
4. Social and Environmental Impact:
- Companies have a responsibility to manage their societal and environmental impacts proactively.
- Positive ESG initiatives can lead to improved community relations, customer loyalty, and overall societal well-being.
ESG Strategy: Data Plays a Crucial Role
Data and sustainability make a perfect combination. Data appears to be the cornerstone for accurate tracking, reporting, and analysis of ESG performance.
By leveraging comprehensive and transparent data, companies can ensure compliance with regulations, enhance stakeholder trust, and drive sustainable growth. Robust data management also facilitates informed decision-making and continuous improvement in ESG initiatives.
Dive deeper and learn how to successfully drive a CSRD/ESG initiative with a data-driven approach in our dedicated article.
CSRD: Challenges and Opportunities
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) introduces extensive requirements for European companies, reshaping how they approach sustainability and ESG management. Here are the key challenges and opportunities presented by the CSRD:
1. Increased Reporting Requirements:
The CSRD mandates detailed disclosures on sustainability matters, including environmental, social, and governance factors. This requires comprehensive data collection and transparency across all operations.
2. Scope and Scale:
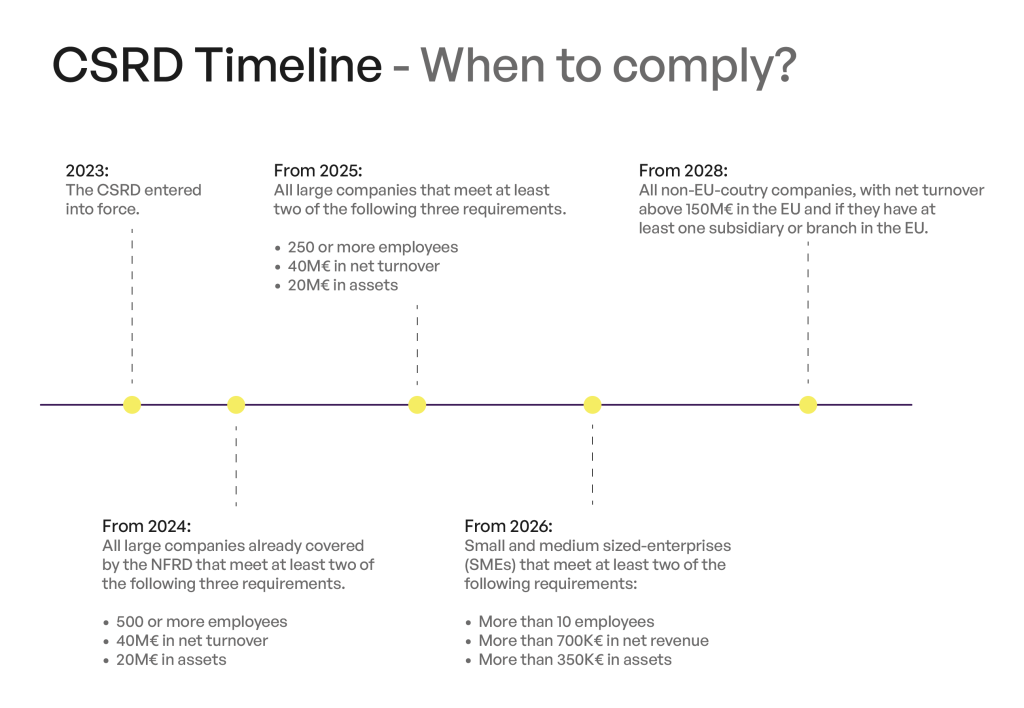
The directive extends to a broader set of large companies and listed SMEs, impacting over 50,000 companies. Compliance deadlines are phased from 2024 to 2029, depending on company size and listing status.
3. Regulatory Risks:
Companies must navigate multiple jurisdictions and emerging regulatory frameworks, including the EU Taxonomy for sustainable economic activities.
4. Human Capital and Workforce Management:
The shift towards hybrid work and the importance of employee well-being and engagement pose significant challenges. Companies need to focus on attracting and retaining talent while addressing human capital risks.
Strategies for Effective CSRD Compliance
Given the complexities of the CSRD, companies must adopt strategic approaches to ensure compliance and leverage the directive as an opportunity for growth and innovation.
1. Early Preparation and Robust Assessment:
- Companies should start by conducting a robust double materiality assessment to determine what they should report. This involves assessing both the impact of the company on environmental and social factors and the impact of these factors on the company.
- Early preparation can help identify potential issues, allowing time for remediation before mandatory requirements come into effect.
2. Engagement with Assurance Providers:
- Working closely with independent assurance providers from the beginning of the reporting journey can provide unbiased perspectives and enhance the quality of reporting.
- Assurance on sustainability reporting has been shown to positively impact company outcomes, including reducing carbon footprints and improving transparency.
3. Collaboration and Benchmarking:
- Engaging with industry peers and working groups can help companies benchmark their efforts, critically assess each other’s determinations, and work through matters of interpretation. This collaboration can enhance comparability and quality reporting.
4. Embedding Processes and Controls:
- Companies should embed robust processes and controls throughout their operations to ensure accurate and comprehensive data collection and reporting.
- Documentation, transparency, and traceability are fundamental concepts that should be applied to all stages of CSRD preparation.
The Path Forward: Embracing ESG and CSRD
The CSRD is more than just a regulatory requirement; it is a strategic opportunity for companies to reframe their business models in the context of sustainability and seek opportunities for value creation. By embracing the principles of ESG and aligning with the CSRD, companies can position themselves as leaders in sustainability, attract investment, and drive long-term growth.
Key Takeaways for Companies:
- Act Now: Delaying action can lead to issues such as process weaknesses and incomplete data. Early preparation is essential.
- Focus on Materiality: Conduct a double materiality assessment to determine which topics are most relevant to report.
- Engage with Experts: Work with assurance providers and industry peers to enhance reporting quality and comparability.
- Embed Sustainability: Integrate ESG principles into all aspects of business operations to drive innovation and sustainable growth.
Conclusion
As the regulatory landscape evolves, businesses must adapt to meet new reporting requirements and leverage these changes as opportunities for growth and innovation. A robust ESG strategy is indispensable for long-term business success, ensuring compliance with evolving regulations like the CSRD, enhancing the company’s reputation, attracting top talent, mitigating risks, and driving sustainable growth. By proactively managing their societal and environmental impacts, companies can improve community relations, customer loyalty, and overall societal well-being.
In conclusion, the CSRD challenges businesses to not only comply with new reporting standards but to transform their operations for a more sustainable future. By starting early, engaging with assurance providers, and embedding robust processes, companies can turn regulatory compliance into a strategic advantage, positioning themselves at the forefront of the sustainability movement.